Table of Contents
The healthcare sector is experiencing a surge of innovation, with cutting-edge technologies reshaping patient care, medical processes, and operational efficiency. As we approach the close of 2024 and prepare for 2025, several transformative trends are set to redefine the sector. These advancements go beyond routine improvements, signaling major shifts in how healthcare providers use technology to enhance care and streamline operations.
Here are the top 10 healthcare technology trends poised to drive the future in 2025 and beyond.
1. Increased focus on internal communication

Healthcare providers face unique communication challenges. From connecting frontline workers and office staff across multiple specialties to ensuring the protection of electronic health records, seamless communication is critical to running a healthcare facility efficiently. Effective communication is crucial to the smooth operation of any healthcare system, ensuring that staff remain informed and engaged, as seen in these successful internal communication examples. And, with teams often spread across different locations and using various devices, the need for streamlined and secure intelligent communication platforms has never been more urgent.
While technologies like remote monitoring, cleaning solutions, and screening tools capture much of the public’s attention, a quieter yet equally critical revolution is happening within healthcare—the modernization of internal communications.
Bridging the gap: Efficient communication for better outcomes
Administrators increasingly rely on advanced internal communication platforms to ensure that the right information reaches the right people—whether frontline workers in the ER, administrative staff, or leadership teams. This real-time communication technology is crucial in day-to-day operations and during crises. By ensuring efficient message delivery, these tools help facilities react quickly to emerging situations, reducing confusion and enhancing care.
Healthcare communication technologies also simplify the process of distributing regulatory updates, policy changes, or urgent notices to staff, ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA. With the ever-present risks to patient data and privacy, communication systems provide an added layer of protection by integrating seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure.
“Healthcare is always complicated, and our system is no exception. We have felt the impact of the work that we do and have seen it both in the stories we tell internally and externally.”
Retention through employee engagement and two-way communication
Employee retention continues to be a major concern in the healthcare sector, but effective communication can be a game-changer. When employees feel informed, supported, and part of the decision-making process, they are likely to stay with the organization. Strong employee engagement, driven by clear and consistent communication, fosters a sense of belonging and helps staff stay connected to the organization’s goals.
By implementing systems that allow for two-way communication, administrators can gather valuable feedback and address issues before they lead to burnout or turnover. These communication platforms also enable leaders to show staff that their voices matter, creating a culture of inclusivity and engagement. In a high-stress industry like healthcare, this sense of connection and community can make a significant difference in both employee engagement and retention rates.
If your facility hasn’t upgraded its internal communication technology, it’s time to consider a solution that can handle the complexities of modern healthcare. Advanced communication platforms not only boost engagement and retention but also improve compliance, operational efficiency, and care.
2. Cybersecurity: Safeguarding healthcare in the digital era

The healthcare sector is a prime target for cyberattacks, with increasingly sophisticated threats emerging in recent years. As healthcare facilities rapidly embraced new technologies to meet the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic, cybersecurity upgrades have often lagged, leaving many organizations vulnerable.
This digital transformation, while essential for improving care, has made healthcare networks an attractive target for hackers.
Data security: The cornerstone of healthcare protection
Protecting patient data and electronic medical records (EMRs) remains a top priority for the healthcare industry. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandates stringent data security standards, requiring facilities to continuously assess their data protection protocols. Given the high value of patient data on the black market, organizations must stay vigilant, adopting cutting-edge cybersecurity solutions to mitigate risks.
Healthcare professionals must also address the increased usage of telemedicine, wearable devices, and connected health systems, which introduce new vulnerabilities. Securing these tools is critical, as they become integral to modern patient care.
Protecting patient privacy in a connected world
With the rise of digital health trends like wearable technology and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), the scope of patient privacy concerns has broadened significantly. While these innovations provide tremendous benefits—such as remote patient monitoring and personalized care—they also introduce new challenges in safeguarding personal health information (PHI).
The medical industry must invest heavily in advanced technologies to ensure patient privacy is not compromised while complying with stringent legal requirements.
Navigating GDPR and HIPAA: Global data protection standards
While HIPAA governs the protection of patient data in the U.S., healthcare providers operating on a global scale must also comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The GDPR, regarded as the toughest privacy law in the world, extends to any organization dealing with data from EU citizens, even if the business operates outside the European Union.
For U.S. providers serving international patients, GDPR compliance is not just a recommendation—it’s a legal obligation. The penalties for non-compliance are severe, making it essential for healthcare organizations to adopt cybersecurity and data privacy measures that meet or exceed HIPAA and GDPR standards.
Looking ahead: The future of cybersecurity in healthcare
As the healthcare industry deepens its investment in digital tools, the demand for robust cybersecurity systems is rising rapidly. Cybersecurity has become one of the top healthcare technology trends, as healthcare organizations must safeguard sensitive patient data while adhering to increasingly stringent privacy regulations.
To meet these challenges, healthcare IT professionals are prioritizing advanced security solutions like cloud-based data storage, VPN protection, and network access management.
3. AI and machine learning: Transforming healthcare

Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are healthcare technology trends rapidly revolutionizing the industry by enabling more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and streamlined operational efficiency. At the core of this transformation is machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence that uses vast amounts of data to “learn” and improve its predictive accuracy over time.
In healthcare, machine learning is being applied in numerous critical areas, offering solutions that were previously unimaginable. For example, ML algorithms are helping to detect early signs of cancer by analyzing complex medical imaging data far more quickly and accurately than human physicians can. These algorithms are also being used to predict patient outcomes, allowing providers to proactively intervene and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Improving diagnosis and treatment
One of the most impactful uses of ML in healthcare is in diagnosing diseases. Artificial intelligence tools can analyze large sets of healthcare data—such as lab results, genetic information, and medical histories—to identify patterns that may signal the onset of a condition long before traditional methods can. This allows for earlier diagnosis, better treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes.
In addition to diagnostics, AI and ML are making strides in personalizing treatment. By analyzing data from previous treatments, outcomes, and patient-specific information, models can suggest tailored therapies that are more likely to be effective. This level of precision medicine improves care while reducing the trial-and-error process typically associated with treatments.
Lowering costs and enhancing operational efficiency
Beyond direct care, machine learning is also optimizing operational aspects of healthcare. Organizations are leveraging artificial intelligence to automate administrative tasks, from medical record-keeping to billing, reducing human error and freeing up workers to focus on more pressing tasks. Additionally, AI-driven solutions can help reduce healthcare costs by predicting resource needs, preventing overstaffing, and minimizing waste.
For example, models can analyze hospital data to predict patient admission rates, enabling better staffing decisions and resource allocation. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances patient satisfaction by reducing wait times and improving care quality.
Supporting, not replacing, healthcare workers
While AI and ML offer significant benefits, they are not replacements for human employees. Instead, these technologies are best viewed as tools that augment the capabilities of medical professionals—like handling time-consuming data analysis and offering recommendations—but human judgment and expertise remain irreplaceable, especially in complex medical decisions.
4. Digital healthcare services: Virtual and augmented reality
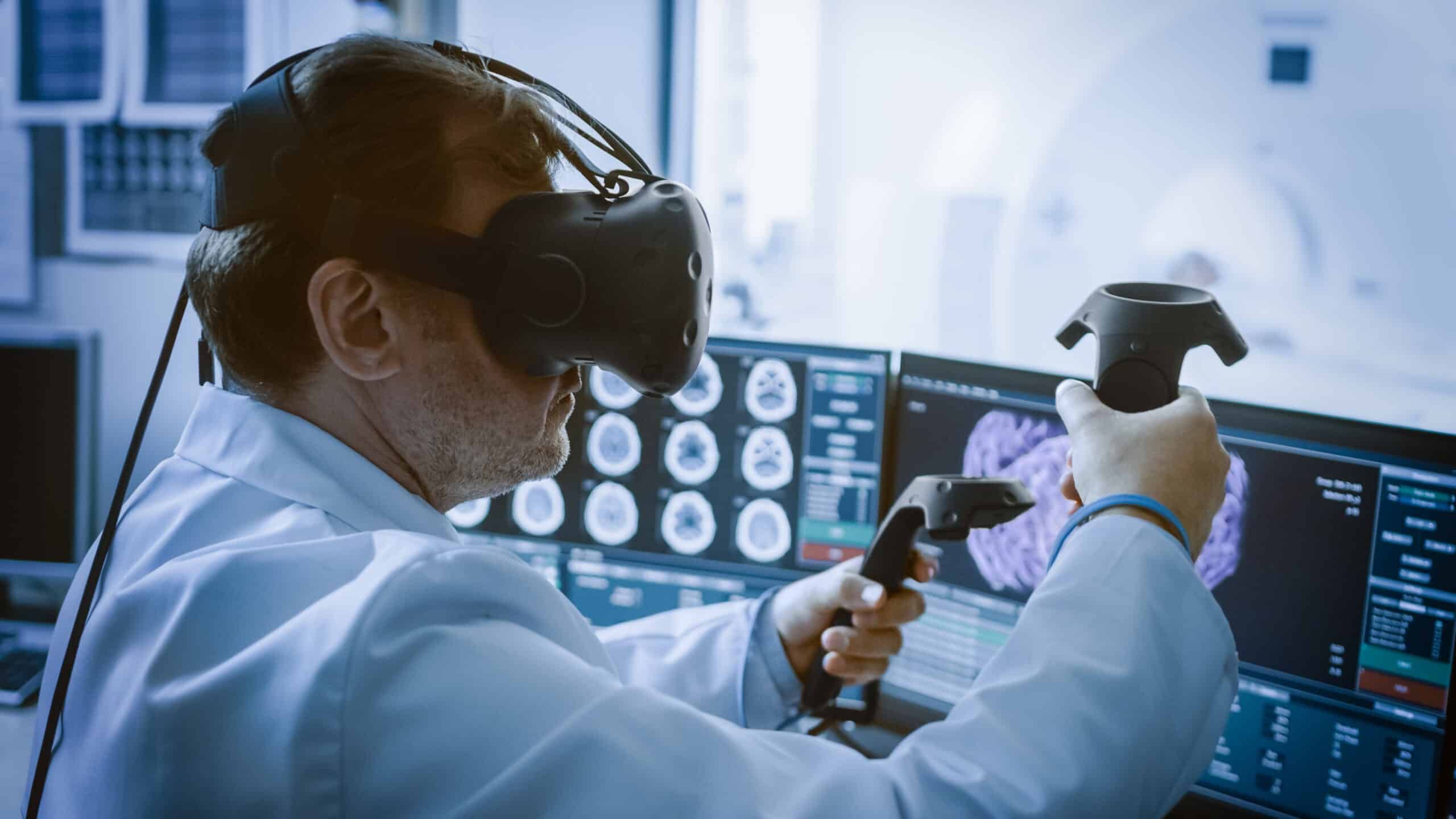
The healthcare industry is embracing digital innovations like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to transform care, education, and operational efficiency. These technologies, once viewed primarily as tools for entertainment, have evolved into powerful resources for a healthcare provider, enabling everything from non-invasive training simulations to advanced patient treatment methods.
Virtual reality in healthcare
Virtual reality, once the domain of video games, is now a growing force in healthcare. As of 2024, the global healthcare virtual reality market is valued at over $4 billion, and that number continues to grow as more medical facilities adopt VR for a range of applications. This technology allows professionals, students, and patients to engage in immersive, simulated environments that provide hands-on experience without risk.
Medical professionals use VR to simulate surgeries, rehearse complex procedures, and train staff. This ability to practice in a risk-free environment is critical for improving surgical outcomes and reducing the likelihood of errors. Beyond education, VR has also made waves in pain management and rehabilitation. For example, one study demonstrated that virtual reality reduced discomfort by over 30% for patients with conditions like low back pain and fibromyalgia.
The impact of VR extends to overcoming mental health challenges as well. The World Health Organization (WHO) predicts that by 2030, mental illness will be the leading burden of disease worldwide. Technologies like virtual reality solutions will play an essential role in creating new, effective care models for mental health. By offering simulated environments for therapy, stress relief, and cognitive behavioral interventions, VR can help patients manage anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions in a controlled, immersive setting.
Augmented reality in healthcare
Augmented reality (AR) is emerging as a vital healthcare technology trend, transforming the way providers interact with patients and medical data by overlaying digital information onto the physical world. This technology is increasingly utilized in hospitals to improve diagnostics, treatment planning, and surgical procedures. For example, AR enables surgeons to access real-time, 3D visualizations of a patient’s anatomy during surgery, allowing for more precise incisions and lowering the risks associated with invasive procedures.
AR-powered tools also enhance patient interactions. Symptom checker chatbots using AR enable patients to describe their symptoms and receive instant feedback, reducing the load on clinical staff and speeding up the triage process. Additionally, AR solutions integrated with artificial intelligence can assist physicians in refining diagnoses by providing alternate possibilities based on real-time analysis of medical data.
Hyper-personalized comms for every employee
“We can send certain communications just to pilots, or in-flight tech ops, or airports, and also target by city or region—slice and dice the content so it’s appropriate for the team member.”
5. Reducing risk through healthcare technology and communication
In the healthcare industry, effective communication is not just a convenience—it’s a vital component of risk management. Poor communication, whether among staff, between departments, or with patients can lead to errors, delays, and even serious medical incidents. However, healthcare technology trends are helping reduce these risks by improving the way information is shared and managed across organizations.
Healthcare leaders recognize that advanced communication platforms are now allowing critical information to reach the right people at the right time. These tools streamline operations, prevent miscommunication, and enhance decision-making processes, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and risk reduction.
Improving coordination and safety with real-time communication
One clear example of how technology improves safety and reduces risk is the story of Cooper University Health Care, which integrated a comprehensive internal communication platform to enhance engagement and reduce risk among its 8,500+ employees. Cooper University Health Care was able to standardize and centralize its internal messaging system, ensuring that critical updates, safety protocols, and real-time information were consistently delivered to frontline workers and medical staff.
With this communication system in place, Cooper addressed several risk factors that stemmed from communication breakdowns. The platform enabled the delivery of safety reminders, policy updates, and important health information with speed and accuracy, ensuring that staff were always up to date and prepared to handle patient needs. By improving communication, they were able to reduce confusion, eliminate costly delays, and enhance care outcomes, all while maintaining compliance with safety regulations.
Reducing risk by engaging healthcare workers
Engagement plays a crucial role in reducing risks, and modern communication platforms are specifically designed to keep workers informed, connected, and engaged. Lehigh Valley Health Network’s employee engagement strategy is another great example of how engagement can reduce risks and keep healthcare workers connected. When staff are fully informed of policies, procedural changes, and patient-specific information, the risk of medical errors, misdiagnoses, and treatment delays decreases significantly.
By implementing tools that facilitate real-time communication and provide personalized, role-specific information, healthcare organizations can ensure that employees feel confident in their decision-making and care delivery. This not only improves patient safety but also reduces the risk of regulatory violations, helping organizations avoid costly penalties and reputational damage.
6. Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring: The future of accessible care

Telemedicine has emerged as a critical component of modern healthcare, revolutionizing the way patients and providers interact by delivering care remotely. By utilizing digital platforms, such as video calls, phone consultations, email, and secure messaging systems, telemedicine enables patients to receive medical attention from the comfort of their homes. This shift has redefined how people access healthcare, reducing the need for in-person visits for non-emergency issues and offering greater convenience for both patients and providers.
The pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, but its benefits have ensured that it will remain a key part of healthcare long into the future. For conditions that don’t require immediate physical intervention—such as routine checkups, follow-ups, or chronic disease management—telemedicine provides a convenient, cost-effective alternative to traditional doctor visits. It also expands access to care for patients in rural or underserved areas, eliminating the barriers of distance and transportation.
Remote patient monitoring: Enhancing ongoing care
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) takes telemedicine a step further by allowing providers to continuously track patients’ health metrics outside the clinic. With the help of wearable devices, mobile apps, and connected home health equipment, RPM enables real-time monitoring of vital signs, medication adherence, and other critical healthcare data. This constant stream of information helps clinicians make informed decisions quickly, potentially preventing complications and reducing hospital readmissions.
Chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease particularly benefit from RPM, as patients can be monitored consistently without the need for frequent in-person appointments. Additionally, RPM can be lifesaving for elderly or high-risk patients, enabling providers to intervene promptly if abnormalities are detected.
Transforming patient outcomes and reducing costs
One of the biggest advantages of telemedicine and remote monitoring is the ability to improve patient outcomes while reducing healthcare costs. By catching potential issues early through RPM and providing immediate virtual consultations, providers can prevent more severe complications that often result in costly hospital visits or extended treatments.
Telemedicine also allows providers to manage a larger volume of patients efficiently, reducing wait times and improving the overall patient experience. This digital shift also empowers patients by offering them more control over their healthcare, as they can easily access their health information, manage appointments, and receive care without the traditional hurdles of scheduling and commuting.
Expanding access and future growth
Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring have expanded access to care for those living in remote areas and increased access for patients facing mobility issues, transportation challenges, or limited time due to work or family commitments. With the increasing integration of artificial intelligence and advanced data analytics, the healthcare industry will likely become even more personalized, offering targeted care based on individual health patterns and needs.
Personalization powers engagement
“Ensuring employees have access to the latest information, and having it personalized to them, is really important. It’s transformed the way that people interact with our comms. Before Firstup, we weren’t able to do that.” BBC
7. Automation of administrative processes: Streamlining efficiency and reducing risk

The automation of administrative processes is one of the most impactful healthcare technology trends, allowing organizations to enhance operational efficiency, minimize manual errors, and free up resources for care.
By automating repetitive tasks—such as scheduling, billing, and patient record management—healthcare providers can streamline workflows, reduce administrative bottlenecks, and improve overall accuracy.
One of the key advantages of automation in healthcare administration is its ability to reduce human error, which can lead to costly mistakes, regulatory violations, or even compromised patient safety. For instance, automating the management of electronic health records (EHR) ensures that patient data remains accurate, up-to-date, and accessible, minimizing the risk of medical errors or treatment delays.
The role of communication platforms in automation
Internal communication platforms play a critical role in supporting automation initiatives. By integrating these platforms with automated systems, professionals can receive real-time notifications about important tasks, policy updates, or patient-specific information. This integration ensures that staff stay informed and can respond promptly to any administrative issues that arise, further reducing risk.
For example, an automated scheduling system integrated with an internal communication platform can notify staff of shift changes or new patient appointments in real time. This ensures healthcare professionals are always up to date on their responsibilities, reducing the likelihood of scheduling conflicts or missed appointments.
Enhancing staff engagement and compliance
Automation also enhances staff engagement by relieving healthcare specialists from time-consuming, repetitive tasks, enabling them to focus on patient care. This not only improves job satisfaction but also enhances overall performance. Automated systems also support compliance by ensuring that staff are updated on new regulations and protocols, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
8. Advancing healthcare with data interoperability and standardization
As healthcare systems become more reliant on digital solutions, data interoperability and standardization have emerged as crucial healthcare technology trends. The ability to seamlessly exchange and interpret healthcare data between providers, medical devices, and healthcare facilities is essential for improving patient outcomes, reducing inefficiencies, and ensuring the smooth operation of healthcare services.
Data interoperability refers to the ability of different systems and technologies to communicate and share information effectively. In the healthcare sector, this means enabling the seamless exchange of electronic health records (EHR), lab results, and other critical health data across various platforms, including legacy medical systems and modern health technologies. When healthcare professionals have immediate access to accurate and up-to-date patient records, they can make better clinical decisions, improve diagnoses, and ultimately enhance healthcare outcomes.
Standardization, on the other hand, ensures that facilities use consistent formats and protocols when managing and sharing data. Without standardization, information can be lost or misinterpreted as it moves between medical institutions, hindering experts’ ability to provide timely, effective care. For example, different medical equipment or software platforms may record patient information in incompatible formats, slowing down data processing and affecting health outcomes.
Overcoming the fragmentation of healthcare systems
One of the main challenges facing healthcare professionals today is the fragmentation of healthcare systems. Many medical facilities still operate systems that don’t easily integrate with newer technologies. This lack of interoperability can lead to errors, delays, and higher costs, as staff are forced to manually transfer or re-enter data between systems.
For example, in remote patient monitoring, wearable devices that track health metrics need to communicate seamlessly with a patient’s electronic health records. When data interoperability is lacking, workers may not have access to the latest health information, which can negatively impact patient care. Ensuring standardized communication between systems can also reduce the risk of medical errors, improve coordination among medical staff members, and enhance the overall efficiency of healthcare operations.
Data interoperability as a driver of health equity
Interoperable systems can also contribute to health equity by ensuring that healthcare professionals across various settings have access to the same patient information, regardless of where the care is delivered. In rural or underserved areas, for example, remote patient care and telehealth services can provide patients with access to healthcare services they may not otherwise receive.
By ensuring that data from these interactions is integrated into a patient’s central record, providers can maintain continuity of care and improve health outcomes for these populations.
How to Engage Your Healthcare Workforce
9. Empowering healthcare providers through digital training and upskilling
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve with rapid technological advancements, the need for ongoing training and upskilling has never been more critical. Digital platforms are revolutionizing how healthcare professionals acquire new skills, stay up-to-date with the latest medical practices, and adapt to emerging healthcare technology trends.
These platforms provide healthcare leaders with flexible, accessible learning environments where they can engage in professional development at their own pace. Whether through virtual reality simulations, interactive e-learning modules, or AI-powered training tools, digital platforms offer a wide range of resources that prepare medical staff to navigate the complexities of modern healthcare.
Flexible, on-demand learning for healthcare professionals
One of the most significant advantages of digital platforms is the flexibility they offer for healthcare workers to access training and upskilling opportunities on-demand. Through online courses, webinars, and interactive e-learning modules, healthcare professionals can learn at their own pace, whether they are improving their understanding of new medical procedures, brushing up on compliance regulations, or acquiring specialized certifications.
These platforms eliminate traditional barriers like geographic limitations or scheduling conflicts, making continuing education more accessible to providers across healthcare systems. With instant access to expert-led courses, professionals can stay current with the latest healthcare trends and improve their skills without sacrificing patient care.
Collaborative learning and peer engagement
Many digital platforms also facilitate collaboration between healthcare professionals, enabling them to connect, share knowledge, and discuss complex medical cases in real-time. This peer-to-peer engagement is a valuable component of digital upskilling, fostering a community of continuous learning and knowledge sharing across healthcare systems.
By participating in discussion forums, attending live Q&A sessions, or engaging in group problem-solving exercises, providers can broaden their perspectives and refine their clinical decision-making skills.
Increasing access to continuing education
In the past, healthcare providers often faced barriers to continuing education due to geographic constraints, high costs, or demanding work schedules. However, digital platforms have eliminated many of these obstacles, allowing healthcare professionals to access training from anywhere in the world. Whether it’s attending webinars, participating in live-streamed workshops, or completing online certifications, digital learning platforms provide the flexibility that modern healthcare workers need.
By reducing these barriers, digital platforms are democratizing access to education and professional development, ultimately benefiting healthcare systems and patient outcomes.
10. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)

The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) refers to a network of interconnected medical devices, software, and applications that communicate with systems and cloud platforms to collect, store, and analyze health data. These devices, ranging from wearable sensors to in-home monitoring systems, allow healthcare providers to remotely track patients’ health metrics in real-time. This technology enhances care by facilitating continuous monitoring of chronic conditions, medication adherence, and post-operative recovery, all without the need for in-person visits.
IoMT devices typically leverage cloud computing platforms like Google Cloud or Amazon Web Services to store the vast amount of data they generate. This data can then be processed and analyzed using AI and predictive analytics to detect patterns, foresee complications, and provide healthcare providers with actionable insights.
As an example of a good use for IoMT, wearable medical technology can continuously monitor vital signs like heart rate or glucose levels, transmitting this information directly to healthcare providers. This constant flow of data allows for timely interventions and personalized care plans, improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions.
Embracing healthcare technology trends for a stronger future
The healthcare industry is undergoing rapid transformation as new healthcare technology trends reshape everything from patient care to administrative processes. From the integration of AI and machine learning to improve diagnoses and operational efficiency, to the automation of routine tasks and the seamless sharing of data through interoperable systems, these advancements are creating a more connected, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare environment.
As workers continue to embrace these top healthcare technology trends, the role of communication platforms becomes even more critical. Effective internal messaging systems are essential for ensuring healthcare professionals remain informed, engaged, and aligned with organizational goals. These platforms facilitate the real-time flow of information vital for reducing risk, improving compliance, and enhancing patient care.
For healthcare organizations seeking to stay ahead of these trends and meet the growing demands of modern digital health solutions, it’s time to invest in a robust communication strategy. If your healthcare organization is looking for a communications platform to make internal messaging more effective and efficient, contact Firstup for a demo today and explore how our solution can help you adapt to these emerging trends in 2025, and beyond.
Deliver a hyper-personalized employee experience at scale
Table of Contents
Related posts
Subscribe via Email
Subscribe to our blog to get insights sent directly to your inbox.
Related posts

Sign up to receive the latest news and resources from Firstup
Firstup delivers personalized communication and data insights to improve the employee experience at every moment that matters